Labels for Safety, Visuals and Facility ID Desktop Printers
Labels for Product, Wire and Lab ID Benchtop Printers
Labels for Safety, Visuals and Facility ID Desktop Printers
Labels for Product, Wire and Lab ID Benchtop Printers
Safety and Facility ID Desktop Printers
Product, Wire and Lab ID Benchtop Printers
Barcode Scanner and Printer Kits
Barcode Scanner and Printer Kits
PaintStripe Floor Marking Stencils
Valve Lockouts & Hose Lockouts
Group Lock Boxes & Permit Control
Brady Safety Lockout Tagout Services
Pipe Marker Accessories & Mounting Brackets
Maintenance and Production Tags
Calculators and Assessment Tools
Product Finders and Data Sheets
Barcode standards are a set of rules and specifications that define how barcodes are created, printed, and read. Much like the universal understanding of time and distance, these standards ensure that barcodes are consistent so data transfer is accurate and efficient. Thanks to barcode standards some of the world’s largest industries, like healthcare, labs and manufacturing are able to easily capture and share information.
Barcode standards play a crucial role in ensuring accuracy, reliability, and efficiency in various industries. Among the prominent barcode standards are ISO and GS1. While both aim to facilitate seamless data capture and tracking, there are key differences between the two, each with its own set of rules and specifications:
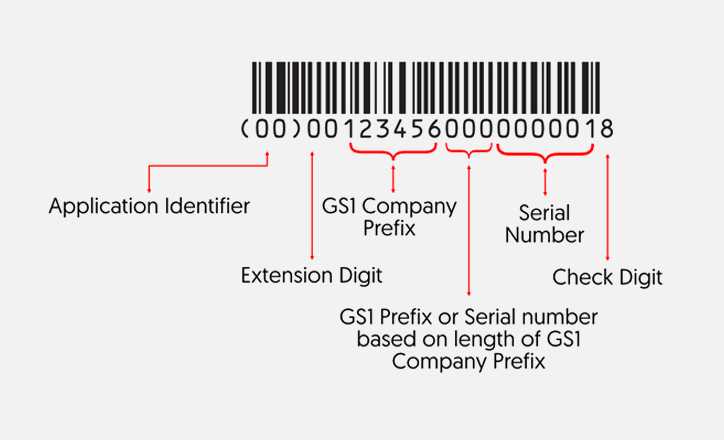
GS1 standards are a set of global barcode standards that have become a worldwide language for supply chain management and product identification. Used in over 150 countries, these standards are recognized by retailers, manufacturers, and logistics providers around the globe.
GS1 standards are based on open standards, which means they’re not proprietary to any one company or organization, but rather supported by a global network of member organizations, which ensures consistency.
To meet the changing needs of the global supply chain, GS1 standards are constantly being updated and improved. They’ve played a major role in the development of the modern supply chain, and continue to be essential for the efficient and accurate movement of goods around the world.
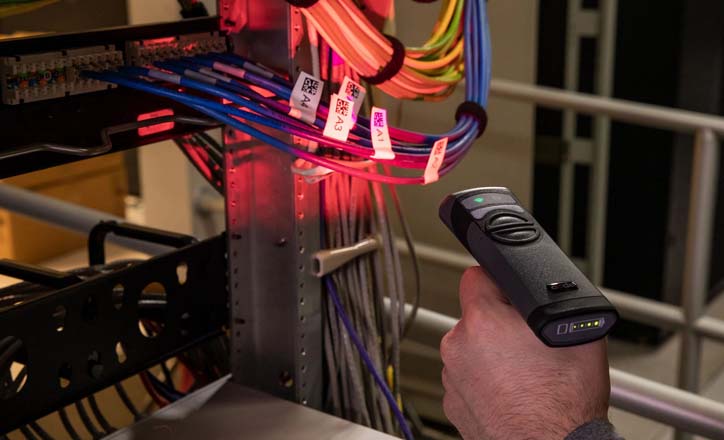

ISO barcode standards are a set of international barcode standards that are developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). While GS1 standards focus on supply chain management, ISO standards focus on the technical specifications and quality requirements of barcodes. They’ve played a crucial role in shipping, receiving, inventory management and tracking of products across many industries.
Today, there are thousands of ISO standards, but when it comes to barcodes there are two prominent ones — ISO/IEC 15416 and ISO/IEC 15415. While they’re both essential for ensuring accuracy, they’re used to define different types of barcodes.
Barcode standards lay down the rules while barcode symbologies define physical characteristics of barcodes such as spacing, height or specific character sets. For example, a barcode standard might specify which barcode symbology must be used for a particular type of product, or which data must be encoded in a barcode. So while there are only a few different barcode standards, there are dozens of different barcode symbologies, each with its own unique characteristics and uses.
Some of the most common barcode standard symbologies include:
Barcodes are composed of several technical elements, like symbologies, that are governed by standards to ensure accuracy. Here's a deep dive into these components:
By adhering to barcode standards, businesses can print and use barcodes effectively, ensuring accurate data capture, efficient supply chain management, and improved product traceability.
Brady has high-performance barcode scanners and labels that meet or exceed industry barcode standards.
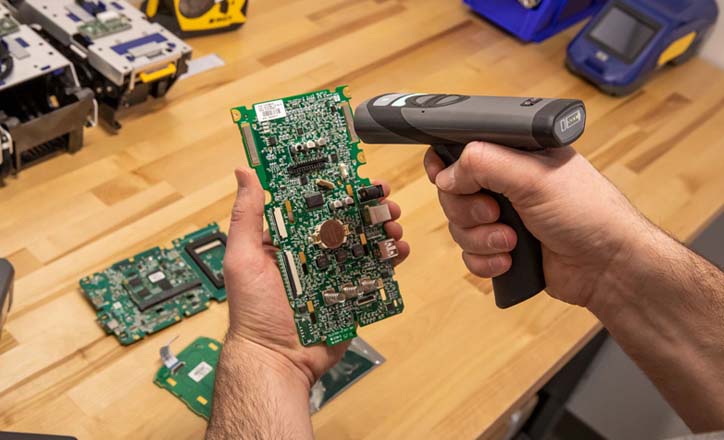

The CR2700 Handheld Barcode Scanner easily reads small barcodes and eliminates time-consuming rescans to keep the job moving. It has the ability to read a wide range of barcode types — like linear, 2D, ID cards and postal — and is designed for asset tracking and general ID in lab and healthcare settings.
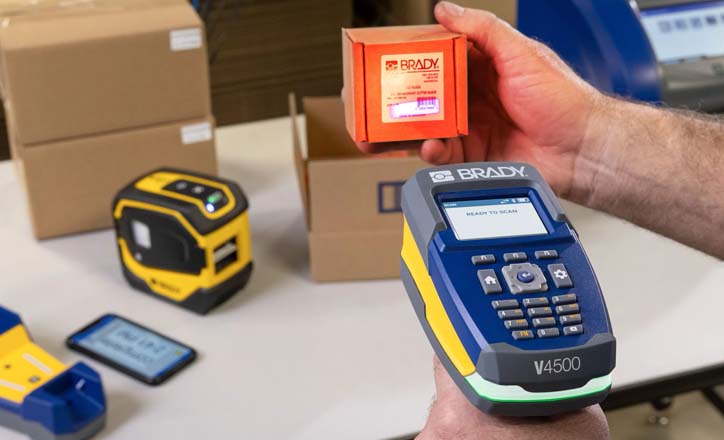

The V4500 Programmable Barcode Scanner is designed to read tiny, shiny and curvy surfaces and features high-speed omnidirectional scanning. It can read a variety of 1D and 2D barcodes on hard-to-read surfaces and is purpose-built for the unique challenges of manufacturing and warehouse tasks.
Barcode standards are constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of businesses and consumers. Here are some of the latest developments and future trends in barcode standards:
Businesses can stay up to date on evolving barcode standards by working with a barcode expert or using verification software.
For many industries, a barcode scanner can serve as a universal solution for compliance and efficiency. With the right scanner, businesses can be confident that the data they collect is accurate, which is especially critical in industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and retail.
Learn more about how Brady's barcode scanners can digitize data capture and automate workflows in a variety of industries.

Confused about barcodes? There are 2 main types: 1D and 2D. This article explains the difference and how they're used in manufacturing, retail, and more.
Discover which barcode is best for your industry
Barcodes streamline workflows, boost productivity, and gain real-time visibility into your operations. From labels and printers to scanners and software, this article gives you everything you need.
Implement a barcode solution today
Level up your barcode scanning with programmable scanners! This article explores the benefits and uses of programmable scanners.
Take control of your data and automate workflows